Originally Published December 2021
Updated September 2023
We considered calling this post “Five Common Cyber-Attacks for Dummies”, but then we changed the title.
The truth is, cyber-attacks happen to many people, and it’s not because they’re “dummies.”
While your IT team may, admittedly, find this list a little basic, it’s likely that many end users in your organization don’t deal with cyber-attacks on a daily basis. We’ve compiled a list of five common cyber-attacks, accompanied by a representative image to help increase familiarity.
Share with your coworkers. Share with your family. Share with your friends. The better we all learn to recognize common cyber-attacks and the threats they pose, the more protected our systems will remain.
1. Phishing
Phishing is when a hacker sends an email trying to trick you into revealing personal and sensitive data. A phishing email appears to be from a trusted source and tries to convince you to give the credentials needed to access your accounts and information.
Phishing emails may have malicious attachments or links to forms that look trustworthy. If you enter the information, the cybercriminals behind the attack access your account.
Common Types of Phishing:
- Spear Phishing: Targets specific individuals or organizations, often using personalized information to increase the likelihood of success.
- Whaling: Focuses on high-profile individuals like CEOs or executives, aiming to access valuable corporate data.
- Vishing: Utilizes phone calls and voice messages to trick victims into disclosing information over the phone.
- Smishing: Involves fraudulent SMS messages that contain links or prompts to reveal sensitive data.
A phishing email might look like something you want to click on, perhaps an attachment or a link to download an invoice, but be cautious. Always make sure you know the sender and are expecting the content.
Otherwise, you’ll be caught like the baby below, who just wanted some pizza, but was tricked with a spoonful of baby food instead.
.gif?width=441&name=giphy%20(1).gif)
2. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s files or locks them out of their system, demanding a ransom be paid in exchange for the decryption key or restoring access.
It’s a significant cybersecurity threat that can cause severe disruptions and financial losses to individuals and organizations.
Common Types of Ransomware:
- Encrypting Ransomware: This type of ransomware encrypts the victim’s files, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid to obtain the decryption key.
- Locker Ransomware: Locker ransomware locks the victim out of their system entirely, denying access to their computer until the ransom is paid.
- Scareware: Scareware displays misleading pop-up messages, often claiming the computer is infected, and urges the victim to pay for fake antivirus software to resolve the non-existent issues.
Victims of ransomware are forced to make an unfortunate decision – either pay the ransom and possibly get the data back, or don’t and lose the data. Targeted organizations will sometimes decide to pay the ransom because they believe this is the only way to get their data back in safe hands.
The hacker behind the attack will promise to restore access to your data once you have paid the ransom, but that doesn’t always happen (after all, cybercriminals by nature are not honest individuals). Another problem with paying the ransom is that it directly funds the development of new and more elaborate ransomware scams.
Of course, prepared victims can restore their systems from a data backup.
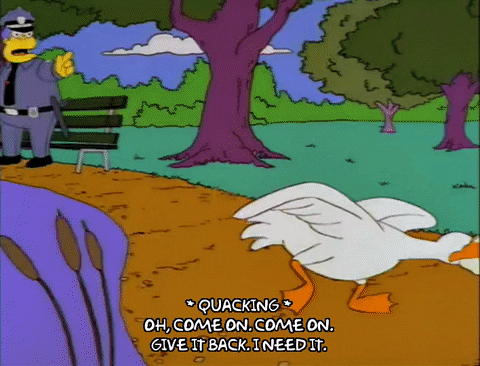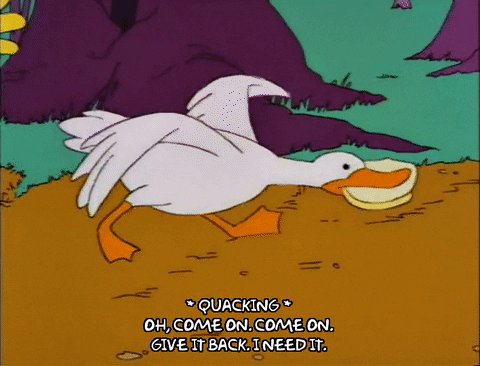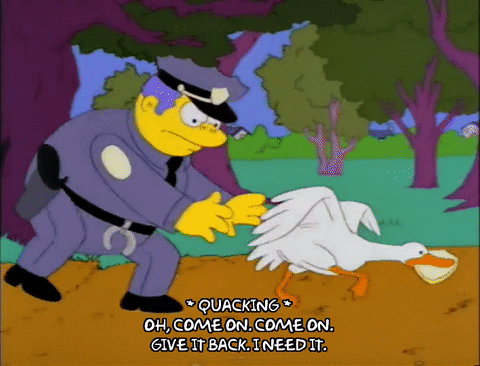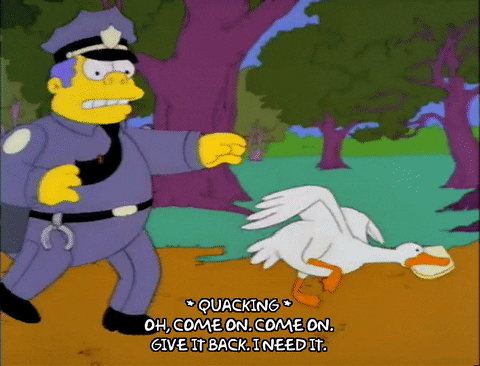
To illustrate a ransomware attack, we look to Chief Wiggum, from The Simpsons, as he attempts to recover stolen goods that he would very much like back.
3. Man in the Middle Attack
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker intercepts and potentially alters the communication between two parties who believe they’re directly communicating with each other.
The attacker positions themselves between the sender and the receiver, allowing them to eavesdrop on the conversation, steal sensitive information or even impersonate one of both parties to manipulate the exchange of data.
Common Types of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
- Passive MITM Attack: The attacker eavesdrops on the communication between the two parties without altering the messages.
- Active MITM Attack: The attacker intercepts and modifies the messages in real-time, allowing them to manipulate the information being exchanged.
The information obtained through a man-in-the-middle attack can be used for many purposes including identity theft, wire transfers or gaining access to accounts through passwords.
The grocery list image below shows how a man-in-the-middle attack works. One person makes a grocery list, but their child intercepts it and alters the information to advance their own agenda (that of acquiring more toys, of course.) Another example of a man-in-the-middle attack would be if your mailman opened your mail and copied the information, then resealed your mail to look like it was never altered.

4. Denial-of-Service (DoS)
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the availability of a target’s services, network or resources, making them inaccessible to legitimate users.
The attacker overwhelms the target’s infrastructure with a flood of traffic, exhausting its resources and causing service interruptions, effectively denying access to genuine users.
Common Types of Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
- Volume-Based Attacks: Flood the target with an enormous volume of traffic, consuming all available bandwidth and server resources.
- Protocol-Based Attacks: Exploit weaknesses in network protocols, causing services to become unresponsive or crash.
- Application Layer Attacks: Target vulnerabilities in specific applications, overwhelming them with requests and rendering them non-functional.
This toll booth traffic jam represents how a flooding DoS attack works (specifically, this would be a Distributed Denial of Service Attack, or DDoS) and how frustrating it can be. The incoming cars represent the “traffic” sent by the attacker to overwhelm a server. In this case, the victim’s server is the toll gate that is trying to process all the traffic. As you can see, the toll gate is not functioning as it should be due to the high amount of traffic.
In an office environment, a DoS attack presents a huge roadblock in your ability to get any work done.

5. Malware
Malware, short for “malicious software,” refers to a wide range of malicious programs designed to infiltrate, damage or compromise computer systems and networks.
Malware is created by cybercriminals to perform various harmful activities, such as stealing sensitive data, disrupting operations or gaining unauthorized access to systems.
Common Types of Malware:
- Ransomware: Encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom for decryption.
- Spyware: Collects sensitive information without the user’s knowledge.
- Rootkits: Conceals malicious activities by manipulating system functions and processes.
- Trojan Horse: Malware disguised as legitimate software, tricking users into installing and executing it.
Trojan Horse attacks can be tricky, as they’re dependent on the user downloading the malware. Much like the Ancient Greek story, a Trojan Horse will appear to be some useful program that you want to download, but it will actually give the hacker control of your system.
A common method used to spread these Trojan Horses is through email attachments (another common phishing ploy). Because the Trojan Horse is already a known illustration, we thought this image with computer-related labels would help explain:

We hope this got you thinking about the various ways hackers can trick you.
Loffler’s IT Solutions Group is a trusted cybersecurity partner for many organizations. Whether your organization is large or small, has full-time IT staff or not, we can help keep your organization secure.

Spencer is the VP of Operations of the IT Solutions Group at Loffler Companies. He has worked in the IT industry for over 25 years, with a focus on IT Managed Services for the past 15 years. He has spent time building custom PCs, designing data center solutions and working with data analytics, as well as writing network monitoring & intrusion detection software. Spencer enjoys music, kayaking and learning about new technology.



